When purchasing LED strip lights, nearly everyone faces the 12V vs 24V choice. However, the differences between them are widely misunderstood. This can lead to confusion and costly mistakes. This article will end that confusion. We will dive deep into every technical detail of the 12V vs 24V LED strip lights debate. Most importantly, we will bust common myths and provide a clear, practical decision framework. After reading, you will be able to choose like an expert.
Busting the Myths
Before we compare, let's clear up three common misconceptions about 12V vs 24V LED strip lights.
Myth 1: "24V is brighter than 12V"
This is completely false. A strip's brightness is determined by its LED chips, density, and total power (wattage), not its voltage. For instance, a 10-watt 12V strip and a 10-watt 24V strip with the same chips will have the exact same brightness.
Myth 2: "24V is more energy-efficient"
This is also incorrect. A 24V system simply achieves the same power by using a higher voltage and a lower current. The total power consumed (watts) remains the same. Therefore, their energy efficiency is on the same level, and your electricity bill will be identical.
Myth 3: "Voltage equals quality"
There is no link between voltage and quality. A strip's quality depends on its core components, like the brand of LED chips and the thickness of its circuit board. High-quality and low-quality products exist in both 12V and 24V formats.

The Core Differences
Now, let's explore the real technical differences between 12V and 24V LED strips. While they may look identical, their internal workings lead to significant performance variations.
Voltage Drop and Maximum Run Length
Above all, the most important difference is how they handle voltage drop.
Term Explained: Voltage Drop
Think of voltage like water pressure in a long garden hose. The pressure is strongest near the faucet but gets weaker at the far end. Similarly, voltage decreases along a long LED strip, causing the far end to be dimmer.(learn more!)
This is where 24V has a massive advantage. Due to the principles of electricity, power loss is calculated as P = I²R (Power Loss = Current Squared x Resistance). Since a 24V system draws only half the current of a 12V system for the same power output, its power loss is only one-quarter as much.
As a result, 24V LED strips can have a much longer maximum run length. For instance, a 24V strip can typically run for 10 meters (32.8 ft) from a single power source with minimal dimming. On the other hand, a 12V strip is usually limited to 5 meters (16.4 ft) before the light at the end becomes noticeably dimmer. Therefore, for large rooms or long architectural features, 24V is the superior technical choice.
Cutting Precision and Customization
However, the longer run length of 24V comes with a practical trade-off: cutting precision.
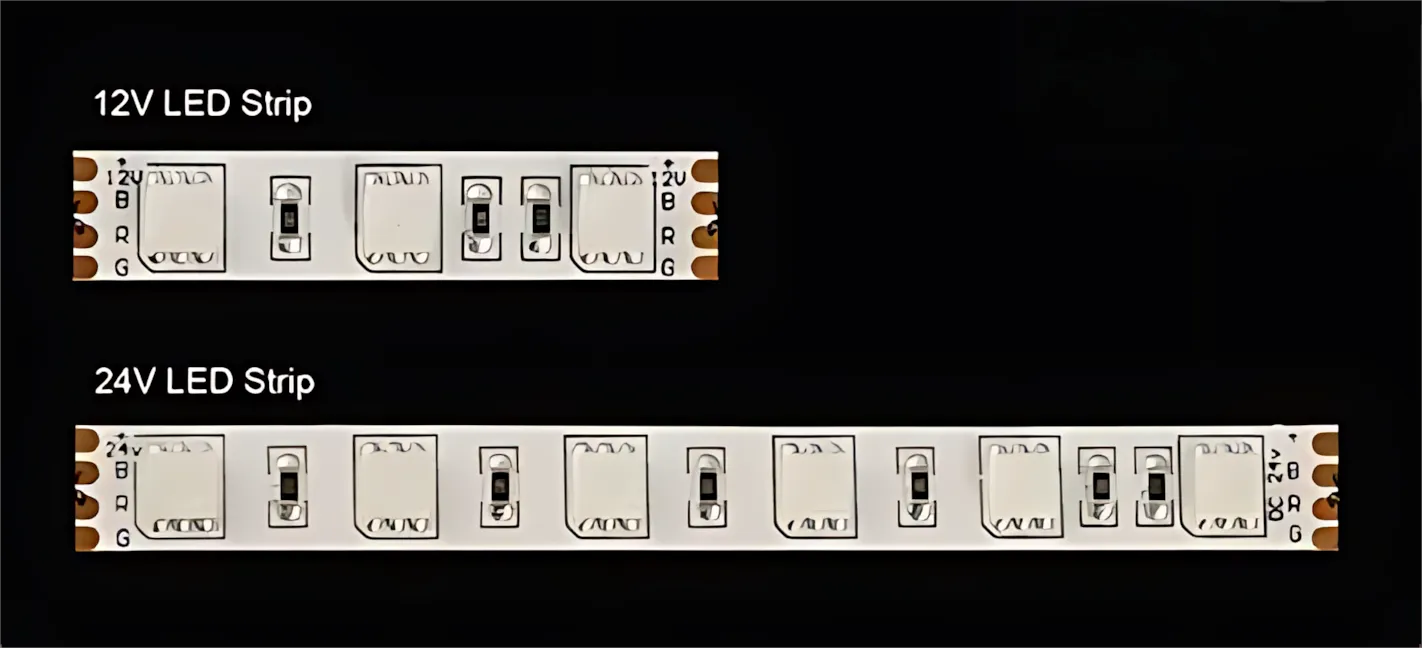
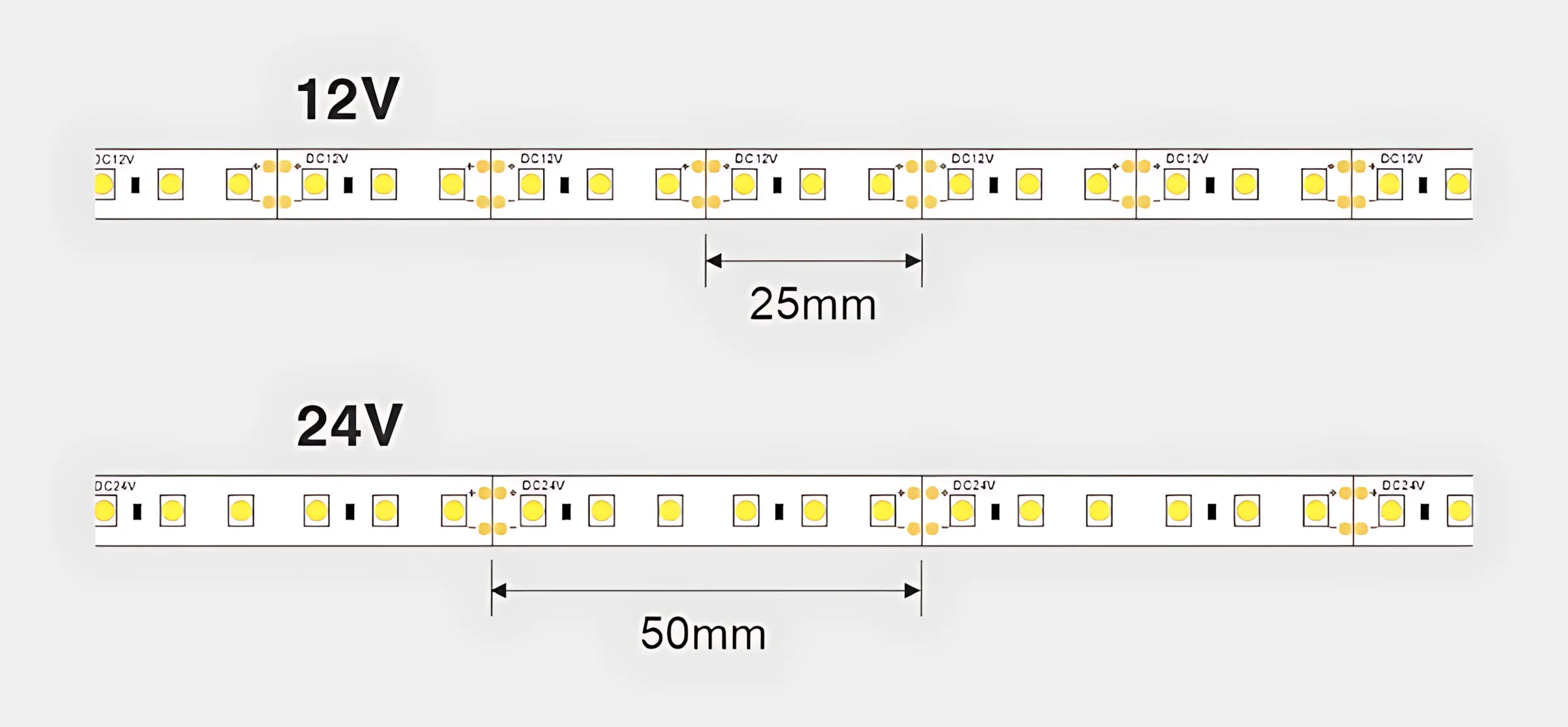
An LED strip is designed with small, independent circuits. A 12V strip usually has its LEDs wired in groups of three. In contrast, a 24V strip typically wires them in groups of six or seven. This is because the voltage has to be "dropped" across several LEDs in a series.
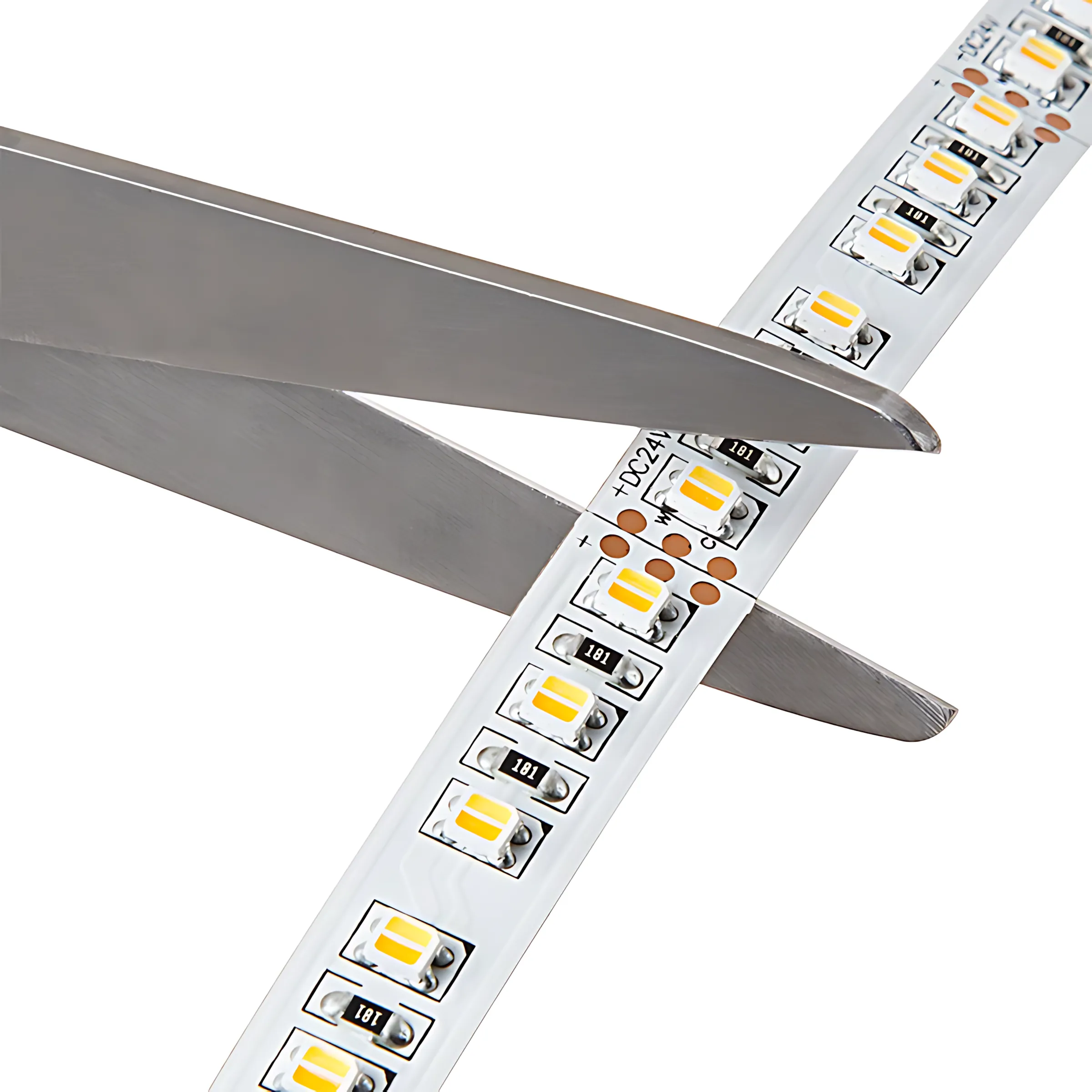
Consequently, 12V strips have cut marks that are much closer together. For example, you might be able to cut a 12V strip every 2.5cm, but a similar 24V strip only every 5cm. That is to say, 12V offers twice the cutting resolution. This makes it the ideal choice for projects that require very precise, custom lengths, like fitting a strip perfectly into a cabinet, a display case, or a tight architectural cove.
Wiring, Current, and Component Stress
Further, the lower current of a 24V system has several cascading benefits for the entire installation.
At the same power level, a 24V system draws half the amperage of a 12V system. This lower current is a significant advantage for two reasons. Firstly, it allows you to use thinner, more discreet, and less expensive wiring to deliver power from the driver to the strip. This is particularly useful in complex installations where wires need to be hidden.
Secondly, and most importantly, lower current means less stress on all components. The copper traces on the strip itself, the solderless connectors, the dimmer or controller, and the power supply all run cooler and are subjected to less electrical strain. This can lead to a more stable, reliable, and longer-lasting lighting system overall, which is why 24V is the preferred standard for professional and commercial-grade installations.
Power Supply Efficiency and Sizing
Finally, there is a subtle but relevant difference in how the power supplies operate. Power supplies (or drivers) have an efficiency curve; they are not equally efficient at all load levels. Most are designed to be most efficient when loaded to about 70-90% of their maximum capacity.
Because 24V systems require fewer, larger power supplies for a large project, it is often easier to size a single 24V driver to run in its optimal efficiency window. In contrast, a large 12V project might require multiple smaller drivers that may not all be running at their peak efficiency. While this difference is minor for small projects, for large-scale commercial installations, it can contribute to measurable long-term energy savings.
Key Advantages of Each Voltage
To make it even clearer, let's summarize the distinct benefits of each system.
Advantages of 12V LED Strip Lights
- Cutting Precision: The shorter distance between cut marks makes 12V strips the superior choice for installations requiring exact custom lengths, such as under-cabinet lighting, shelf lighting, or fitting into tight coves.
- Broad Compatibility with 12V Systems: They are natively compatible with the 12V DC systems found in all cars, RVs, boats, and many off-grid solar power setups. This makes integration in these environments extremely simple.
- Wider Range of Small Accessories: Due to its long history in the DIY electronics space, there is a slightly wider variety of small, low-power accessories like mini-dimmers and battery packs designed for 12V.
Advantages of 24V LED Strip Lights
- Longer Run Lengths: This is their number one advantage. The ability to run a single strip up to 10 meters (or more) with minimal voltage drop simplifies wiring dramatically for large projects.
- Lower Current & Thinner Wires: The reduced amperage means you can use thinner, more discreet, and less expensive wiring to deliver power, which is a major benefit in architectural installations.
- Increased Stability: Lower current results in less power loss and less heat generated in the wiring, leading to a more stable and efficient system, especially for high-power applications.
How to Choose the Right Voltage
So, how do you decide which is right for your project? Let's break it down by your specific needs.
Consider Your Installation Layout
The first question to ask is: do you need a continuous, seamless run of light that is longer than 5 meters (16.4 ft)? If the answer is yes, 24V is the clear winner. It will simplify your wiring and reduce the number of power supplies needed. But, if your project consists of many shorter, separate pieces, then either voltage will work well.
Consider Your Brightness and Power
While voltage doesn't equal brightness, high-power strips with a very high lumen output are generally better suited for a 24V system. The lower current drawn by a 24V strip makes it more stable and efficient at handling the demands of high-wattage applications. In other words, for the brightest strips, 24V is the more robust choice.
Consider Your Cutting Needs
Finally, ask yourself how precise your measurements need to be. Are you fitting the strip into a custom-built cabinet or a tight architectural cove? If you need to cut the strip to a very exact length, the more frequent cut marks of a 12V strip will provide you with much greater flexibility and prevent awkward gaps.

Quick Comparison Table
Feature | 12V LED Strip | 24V LED Strip |
|---|---|---|
Max Run Length | Shorter (Typically 5m) | Longer (Typically 10m) |
Cutting Precision | Higher (Cut marks are closer together) | Lower (Cut marks are further apart) |
Current Draw | Higher | Lower (Allows for thinner wires) |
Best Application | Cars, RVs, projects needing precise cuts | Long runs, architectural & commercial jobs |
Conclusion
In conclusion, the 12V vs 24V LED strip lights debate is not about which is better, but which is more suitable for the task. To sum up, it is a classic engineering trade-off. 24V offers the advantage of 'Length', while 12V offers the advantage of 'Precision'. By understanding these core differences, you now have all the knowledge you need to confidently select the voltage that is a perfect match for your project's goals, budget, and design.
Frequently Asked Questions (Q&A)
1. Can I mix 12V and 24V components?
Absolutely not. This is a strict rule. A 12V strip must use a 12V power supply, and a 24V strip must use a 24V one. Mixing voltages will instantly destroy the lower-voltage component.
2. What happens if I use the wrong voltage?
If you connect a 12V strip to a 24V power supply, it will be overpowered and burn out immediately. If you connect a 24V strip to a 12V power supply, it will be underpowered and will likely be very dim or not light up at all.
3. Do I need a special power supply for a 24V strip?
Not a special one, just a matching one. LED drivers are widely available in many different voltage outputs. You simply need to ensure the driver's output voltage is the same as your strip's required input voltage.










